Did you know that you can navigate the posts by swiping left and right?
How To Force HTTPS on Amazon Elastic Beanstalk Using .Ebextensions
29 May 2017
. category:
devops
.
Comments
#sysadmin
#devops
#aws
#amazon elastic beanstalk
#https
#nginx
#ssl
#docker
AWS Elastic Beanstalk is powerful deployment tools on AWS. It allows users to create applications and push them to a definable set of AWS services, including Amazon EC2, RDS, SNS, CloudWatch, Auto Scaling Group, Elastic Load Balancer.
Some of Elastic Beanstalk resources can be customized using .ebextensions script. Now, we will configure the ELB to proxy HTTP and HTTPS request to different EC2 instance’s ports.
- Configure Elastic Beanstalk to allow both HTTP and HTTPS. Make sure to set an SSL certificate. This will require a refresh of the Elastic Load Balancer.
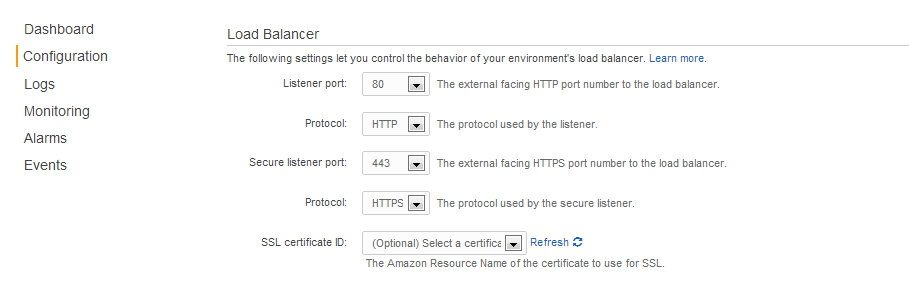
Now your application should be accessible by both HTTP and HTTPS.
-
I am running application through docker, therefore, our application uses the Nginx proxy which can be used to redirect HTTP to HTTPS endpoint. The easiest way to do this is to create a custom configuration file which creates the re-write rules.
-
Create a configuration file inside a “.ebextensions” directory. In my case, the file name is 04_nginx-proxy-https.config with beelow content:
files:
/etc/nginx/sites-available/elasticbeanstalk-nginx-docker-proxy.conf:
content: |
map $http_upgrade $connection_upgrade {
default "upgrade";
"" "";
}
server {
listen 80;
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_types text/html text/plain text/css application/json application/x-javascript text/xml application/xml application/xml+rss text/javascript;
if ($time_iso8601 ~ "^(\d{4})-(\d{2})-(\d{2})T(\d{2})") {
set $year $1;
set $month $2;
set $day $3;
set $hour $4;
}
access_log /var/log/nginx/healthd/application.log.$year-$month-$day-$hour healthd;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
if ($http_x_forwarded_proto != "https") {
rewrite ^(.*)$ https://$host$1 permanent;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://docker;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection $connection_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
group: root
mode: "000755"
owner: root
- Deloy your application with the new config files.
- Reload Nginx (or rebuild the environment) to pick up the change
service nginx reload
