Did you know that you can navigate the posts by swiping left and right?
How To Receive Email Using Amazon SES
07 Jun 2017
. category:
devops
.
Comments
#sysadmin
#devops
#aws
#SES
#lambda
#email
#S3
#DNS
Amazon has a lot of services but we only need 3 of them to solve email receipt problem and not one involves setting up a server. The hardest part is keeping track of all the open tabs.
- Amazon Simple Email Service (SES) was originally built to handle the sending of transaction emails.
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a place to store things. In this case, it will be where we drop incoming emails to be processed.
- Amazon Lambda is the cool tool and allow for serverless computing. We define a function and are charged only for the computing time that the function actually uses.
To get through this, you’re going to need a verified Amazon SES with your domain’s DNS setting.
Part I: Verified domain’s DNS
- Go to SES via the AWS console and select Domains under Identity Management.
- Click on Verify a New Domain at the top of the screen.
- Enter the root of domain you’re verifying, in my case: gluesolution.xyz. Check the Generate DKIM Settings options, and click Verify this Domain
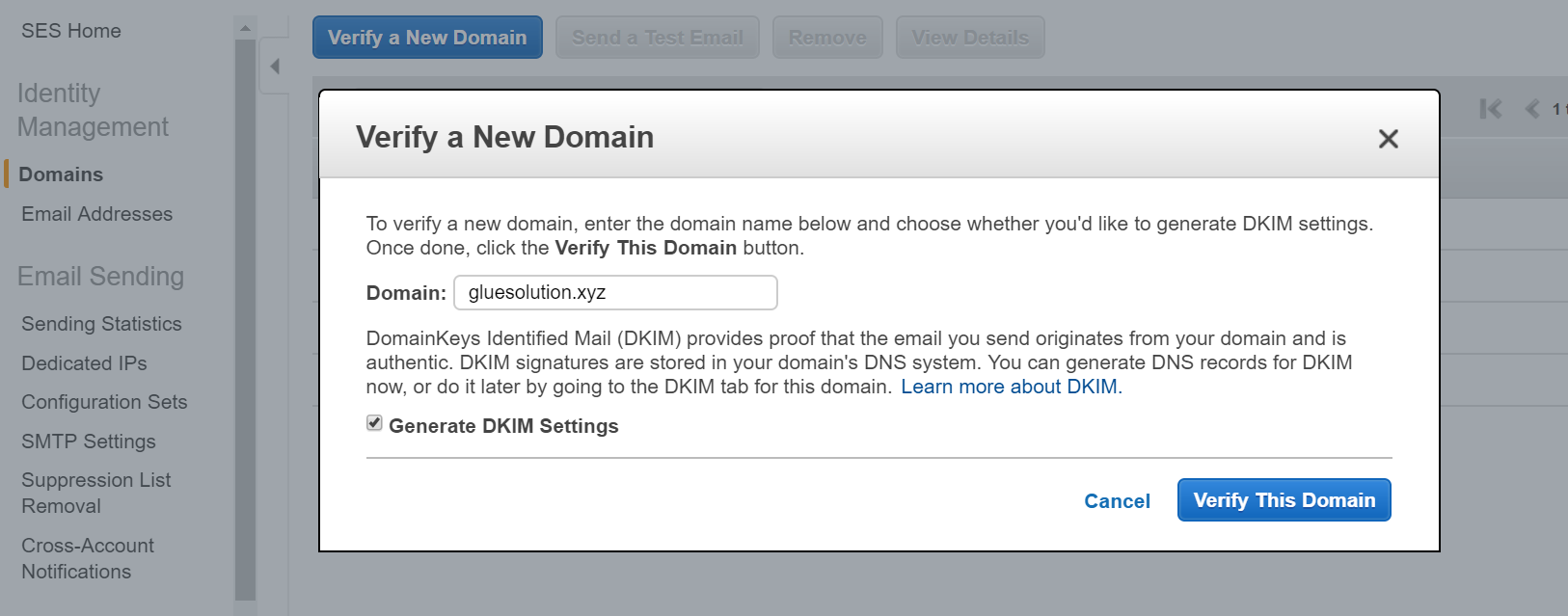
- You’ll be presented with an overlay containing the new records that need to be attached to your domain as part of your DNS configuration. Carefully enter all of these as any mistakes may add extra time to verification process.
- A TXT record acts as domain verification.
- Three CNAME records for the DKIM record set, which SES rotates through automatically.
- And an MX record to route incomming email on your domain to AWS.
In a meantime, you’ll want to verify any email address that you will be forwarding email to. As part of the initial SES configuration, you’re locked in the Amazon SES Sandbox and can only send emails to address you have verified ahead of time. To remove Sandbox, we have to contact AWS. Easy to do that just provide them the right reason.
Part II: Configure SES to receive and forward email
- Once domain verification has processed, click on Rule Sets under Email Receiving on the left.
- Click on View Active Rule Set to view the default rule set. If a default rule set does not exist, create a new one.
- Click Create Rule to create a receipt rule for this domain.
- For receipt, enter the base of your domain (e.g. gluesolution.xyz) rather than a full email address so that all addresses at that domain will match. Click Next Step.
- Select S3 at the first action.
- Choose Create S3 bucket in the S3 Bucket dropdown and enter a bucket name. Click Create Bucket.
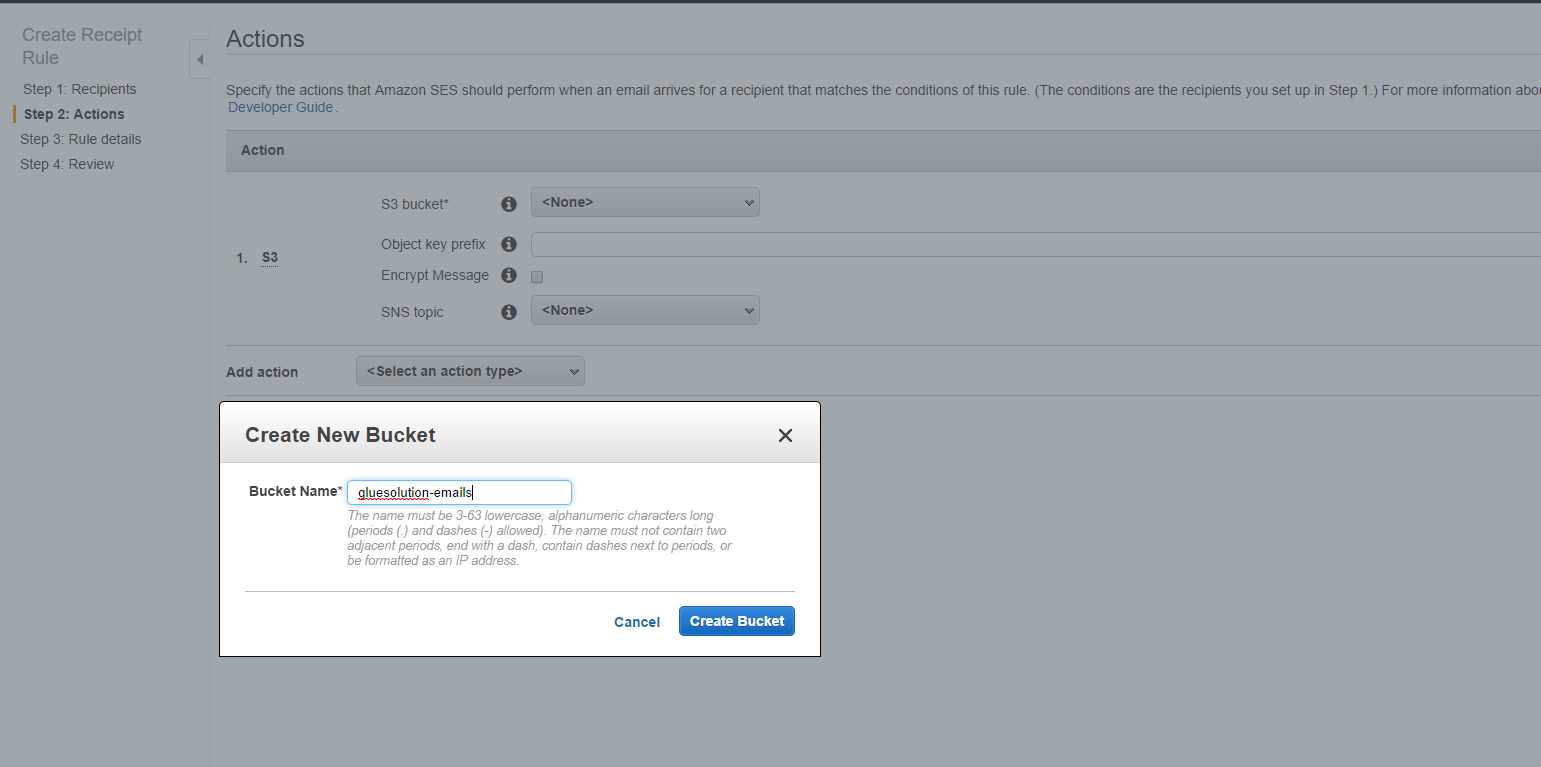
- Leave Object key prefix blank and Encrypt Message unchecked.
- Choose Create SNS Topic in the SNS Topic dropdown and enter a Topic Name and Display Name. Click Create Topic.
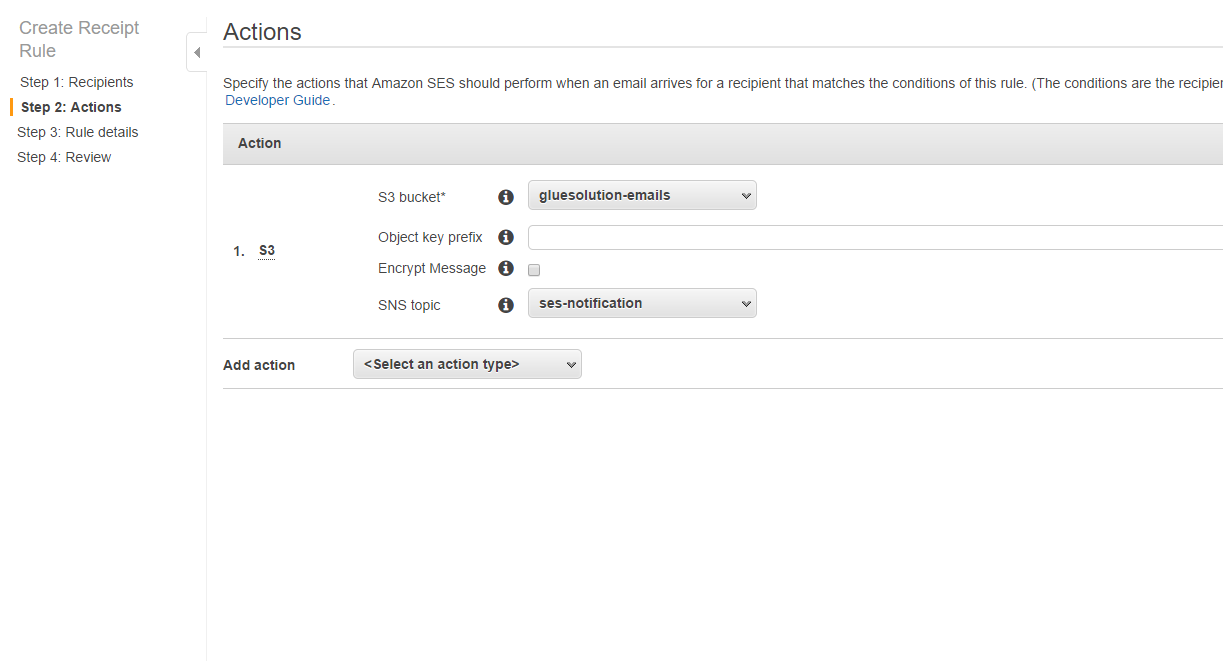
- Click Next Step. We’ll need to do some things before adding the Lambda function.
- Give the rule a name, make sure Enabled is checked, Require TLSis unchecked, and Enable spam and virus scanning is checked. Click Next Step.
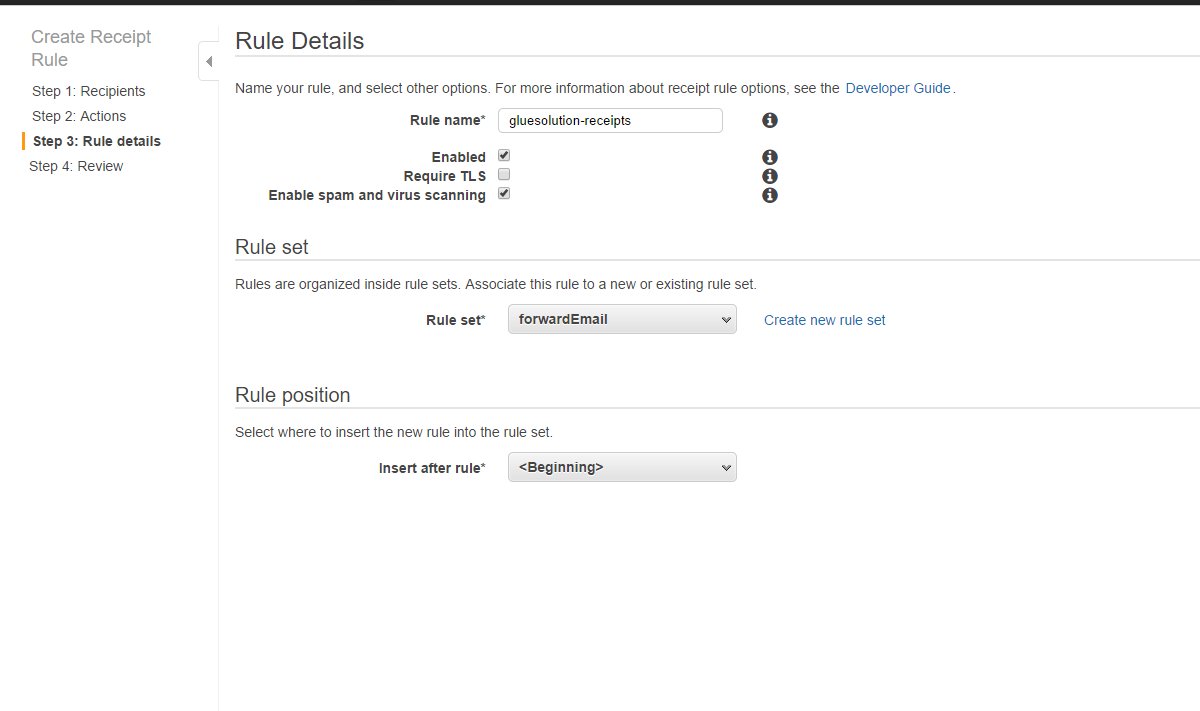
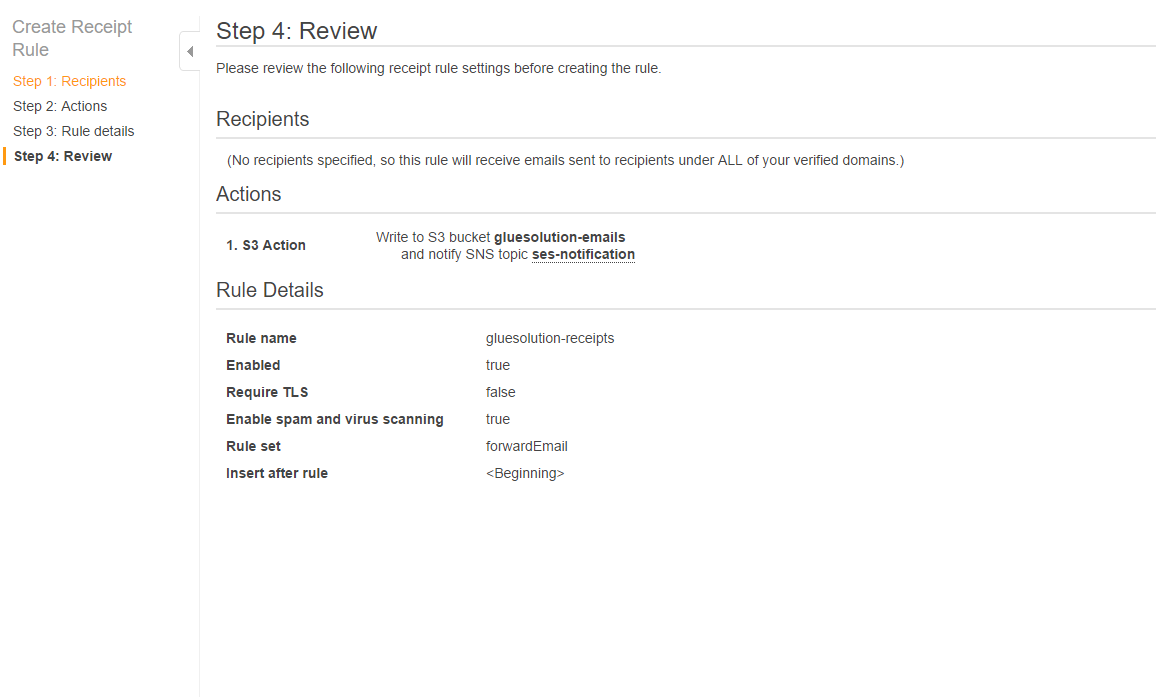
- Review the details and click Create Rule
Part III: Create Lambda function
- Click Create a lamdba function
- Click Skip on the next screen without selecting a blueprint.
- Enter a name and description for the function. Make sure Runtime is set at Node.js 4.3. Paste the below content into the Lambda function code area.
"use strict";
var AWS = require('aws-sdk');
console.log("AWS Lambda SES Forwarder // @arithmetric // Version 4.1.0");
// Configure the S3 bucket and key prefix for stored raw emails, and the
// mapping of email addresses to forward from and to.
//
// Expected keys/values:
//
// - fromEmail: Forwarded emails will come from this verified address
//
// - subjectPrefix: Forwarded emails subject will contain this prefix
//
// - emailBucket: S3 bucket name where SES stores emails.
//
// - emailKeyPrefix: S3 key name prefix where SES stores email. Include the
// trailing slash.
//
// - forwardMapping: Object where the key is the lowercase email address from
// which to forward and the value is an array of email addresses to which to
// send the message.
//
// To match all email addresses on a domain, use a key without the name part
// of an email address before the "at" symbol (i.e. `@example.com`).
//
// To match a mailbox name on all domains, use a key without the "at" symbol
// and domain part of an email address (i.e. `info`).
var defaultConfig = {
fromEmail: "noreply@gluesolution.xyz",
subjectPrefix: "",
emailBucket: "gluesolution-emails",
emailKeyPrefix: "",
forwardMapping: {
"@gluesolution.xyz": [
"gluesolution@gmail.com"
],
}
};
/**
* Parses the SES event record provided for the `mail` and `receipients` data.
*
* @param {object} data - Data bundle with context, email, etc.
*
* @return {object} - Promise resolved with data.
*/
exports.parseEvent = function(data) {
// Validate characteristics of a SES event record.
if (!data.event ||
!data.event.hasOwnProperty('Records') ||
data.event.Records.length !== 1 ||
!data.event.Records[0].hasOwnProperty('eventSource') ||
data.event.Records[0].eventSource !== 'aws:ses' ||
data.event.Records[0].eventVersion !== '1.0') {
data.log({message: "parseEvent() received invalid SES message:",
level: "error", event: JSON.stringify(data.event)});
return Promise.reject(new Error('Error: Received invalid SES message.'));
}
data.email = data.event.Records[0].ses.mail;
data.recipients = data.event.Records[0].ses.receipt.recipients;
return Promise.resolve(data);
};
/**
* Transforms the original recipients to the desired forwarded destinations.
*
* @param {object} data - Data bundle with context, email, etc.
*
* @return {object} - Promise resolved with data.
*/
exports.transformRecipients = function(data) {
var newRecipients = [];
data.originalRecipients = data.recipients;
data.recipients.forEach(function(origEmail) {
var origEmailKey = origEmail.toLowerCase();
if (data.config.forwardMapping.hasOwnProperty(origEmailKey)) {
newRecipients = newRecipients.concat(
data.config.forwardMapping[origEmailKey]);
data.originalRecipient = origEmail;
} else {
var origEmailDomain;
var origEmailUser;
var pos = origEmailKey.lastIndexOf("@");
if (pos === -1) {
origEmailUser = origEmailKey;
} else {
origEmailDomain = origEmailKey.slice(pos);
origEmailUser = origEmailKey.slice(0, pos);
}
if (origEmailDomain &&
data.config.forwardMapping.hasOwnProperty(origEmailDomain)) {
newRecipients = newRecipients.concat(
data.config.forwardMapping[origEmailDomain]);
data.originalRecipient = origEmail;
} else if (origEmailUser &&
data.config.forwardMapping.hasOwnProperty(origEmailUser)) {
newRecipients = newRecipients.concat(
data.config.forwardMapping[origEmailUser]);
data.originalRecipient = origEmail;
}
}
});
if (!newRecipients.length) {
data.log({message: "Finishing process. No new recipients found for " +
"original destinations: " + data.originalRecipients.join(", "),
level: "info"});
return data.callback();
}
data.recipients = newRecipients;
return Promise.resolve(data);
};
/**
* Fetches the message data from S3.
*
* @param {object} data - Data bundle with context, email, etc.
*
* @return {object} - Promise resolved with data.
*/
exports.fetchMessage = function(data) {
// Copying email object to ensure read permission
data.log({level: "info", message: "Fetching email at s3://" +
data.config.emailBucket + '/' + data.config.emailKeyPrefix +
data.email.messageId});
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
data.s3.copyObject({
Bucket: data.config.emailBucket,
CopySource: data.config.emailBucket + '/' + data.config.emailKeyPrefix +
data.email.messageId,
Key: data.config.emailKeyPrefix + data.email.messageId,
ACL: 'private',
ContentType: 'text/plain',
StorageClass: 'STANDARD'
}, function(err) {
if (err) {
data.log({level: "error", message: "copyObject() returned error:",
error: err, stack: err.stack});
return reject(
new Error("Error: Could not make readable copy of email."));
}
// Load the raw email from S3
data.s3.getObject({
Bucket: data.config.emailBucket,
Key: data.config.emailKeyPrefix + data.email.messageId
}, function(err, result) {
if (err) {
data.log({level: "error", message: "getObject() returned error:",
error: err, stack: err.stack});
return reject(
new Error("Error: Failed to load message body from S3."));
}
data.emailData = result.Body.toString();
return resolve(data);
});
});
});
};
/**
* Processes the message data, making updates to recipients and other headers
* before forwarding message.
*
* @param {object} data - Data bundle with context, email, etc.
*
* @return {object} - Promise resolved with data.
*/
exports.processMessage = function(data) {
var match = data.emailData.match(/^((?:.+\r?\n)*)(\r?\n(?:.*\s+)*)/m);
var header = match && match[1] ? match[1] : data.emailData;
var body = match && match[2] ? match[2] : '';
// Add "Reply-To:" with the "From" address if it doesn't already exists
if (!/^Reply-To: /mi.test(header)) {
match = header.match(/^From: (.*\r?\n)/m);
var from = match && match[1] ? match[1] : '';
if (from) {
header = header + 'Reply-To: ' + from;
data.log({level: "info", message: "Added Reply-To address of: " + from});
} else {
data.log({level: "info", message: "Reply-To address not added because " +
"From address was not properly extracted."});
}
}
// SES does not allow sending messages from an unverified address,
// so replace the message's "From:" header with the original
// recipient (which is a verified domain)
header = header.replace(
/^From: (.*)/mg,
function(match, from) {
var fromText;
if (data.config.fromEmail) {
fromText = 'From: ' + from.replace(/<(.*)>/, '').trim() +
' <' + data.config.fromEmail + '>';
} else {
fromText = 'From: ' + from.replace('<', 'at ').replace('>', '') +
' <' + data.originalRecipient + '>';
}
return fromText;
});
// Add a prefix to the Subject
if (data.config.subjectPrefix) {
header = header.replace(
/^Subject: (.*)/mg,
function(match, subject) {
return 'Subject: ' + data.config.subjectPrefix + subject;
});
}
// Replace original 'To' header with a manually defined one
if (data.config.toEmail) {
header = header.replace(/^To: (.*)/mg, () => 'To: ' + data.config.toEmail);
}
// Remove the Return-Path header.
header = header.replace(/^Return-Path: (.*)\r?\n/mg, '');
// Remove Sender header.
header = header.replace(/^Sender: (.*)\r?\n/mg, '');
// Remove all DKIM-Signature headers to prevent triggering an
// "InvalidParameterValue: Duplicate header 'DKIM-Signature'" error.
// These signatures will likely be invalid anyways, since the From
// header was modified.
header = header.replace(/^DKIM-Signature: .*\r?\n(\s+.*\r?\n)*/mg, '');
data.emailData = header + body;
return Promise.resolve(data);
};
/**
* Send email using the SES sendRawEmail command.
*
* @param {object} data - Data bundle with context, email, etc.
*
* @return {object} - Promise resolved with data.
*/
exports.sendMessage = function(data) {
var params = {
Destinations: data.recipients,
Source: data.originalRecipient,
RawMessage: {
Data: data.emailData
}
};
data.log({level: "info", message: "sendMessage: Sending email via SES. " +
"Original recipients: " + data.originalRecipients.join(", ") +
". Transformed recipients: " + data.recipients.join(", ") + "."});
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
data.ses.sendRawEmail(params, function(err, result) {
if (err) {
data.log({level: "error", message: "sendRawEmail() returned error.",
error: err, stack: err.stack});
return reject(new Error('Error: Email sending failed.'));
}
data.log({level: "info", message: "sendRawEmail() successful.",
result: result});
resolve(data);
});
});
};
/**
* Handler function to be invoked by AWS Lambda with an inbound SES email as
* the event.
*
* @param {object} event - Lambda event from inbound email received by AWS SES.
* @param {object} context - Lambda context object.
* @param {object} callback - Lambda callback object.
* @param {object} overrides - Overrides for the default data, including the
* configuration, SES object, and S3 object.
*/
exports.handler = function(event, context, callback, overrides) {
var steps = overrides && overrides.steps ? overrides.steps :
[
exports.parseEvent,
exports.transformRecipients,
exports.fetchMessage,
exports.processMessage,
exports.sendMessage
];
var data = {
event: event,
callback: callback,
context: context,
config: overrides && overrides.config ? overrides.config : defaultConfig,
log: overrides && overrides.log ? overrides.log : console.log,
ses: overrides && overrides.ses ? overrides.ses : new AWS.SES(),
s3: overrides && overrides.s3 ?
overrides.s3 : new AWS.S3({signatureVersion: 'v4'})
};
Promise.series(steps, data)
.then(function(data) {
data.log({level: "info", message: "Process finished successfully."});
return data.callback();
})
.catch(function(err) {
data.log({level: "error", message: "Step returned error: " + err.message,
error: err, stack: err.stack});
return data.callback(new Error("Error: Step returned error."));
});
};
Promise.series = function(promises, initValue) {
return promises.reduce(function(chain, promise) {
if (typeof promise !== 'function') {
return Promise.reject(new Error("Error: Invalid promise item: " +
promise));
}
return chain.then(promise);
}, Promise.resolve(initValue));
};
- fromEmail should be something like noreply@gluesolution.xyz.
- emailBucket should be the name of the S3 bucket you created earlier.
- emailKeyPrefix should be an empty string.
- forwardMaping is used to configure one or more relationships between the incomning email address and the one the email is forwarded to. Use something like @gluesolution.xyz as a catch-all for the last rule.
- Leave Handler set to index.handler.
- Select Basic Execution Role from the role list. A new window will appear to grant Lambda permissions to other AWS resources.
- Choose Create a new IAM Role from the IAM Role drop down and provide a Role Name.
- Click View Policy Document and then Edit to edit the policy document. Copy and paste the below policy document, make sure to change the S3 bucket name in that policy to match yours.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "ses:SendRawEmail",
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::S3-BUCKET-NAME/*"
}
]
}
- Click Allow. You should be transferred back to the Lambda screen.
- Under Advance Settings, set Memory to 128MB and Timeout to 10 seconds. You can leave VPC set to No VPC.
- Click Next
- Review the new function details and click Create function.
Part IV: Add Lambda function to the email receiving rule
- Click Rule Sets under Email Receiving and then View Active Rule Set to seethe existing rules.
- Click on the name of the rule from the previous steps.
- Select Lambda as an action type next to Lambda function
- Select the new function you created next to Lambda function. Leave Event selected for the Invocation type. Leave None selected for SNS topic.
- Click Save Rule
- A permission overlay will appear to request access for SES to invoke the function on Lambda. Click Add permissions.
If someone send to @gluesolution.xyz, it is now receive by Amazon SES. The email is then processed and stored as an object in Amazon S3. SES then notifies Amazon Lambda, which fires the stored function used to process that email and forward it via SES to the mapped email address.
